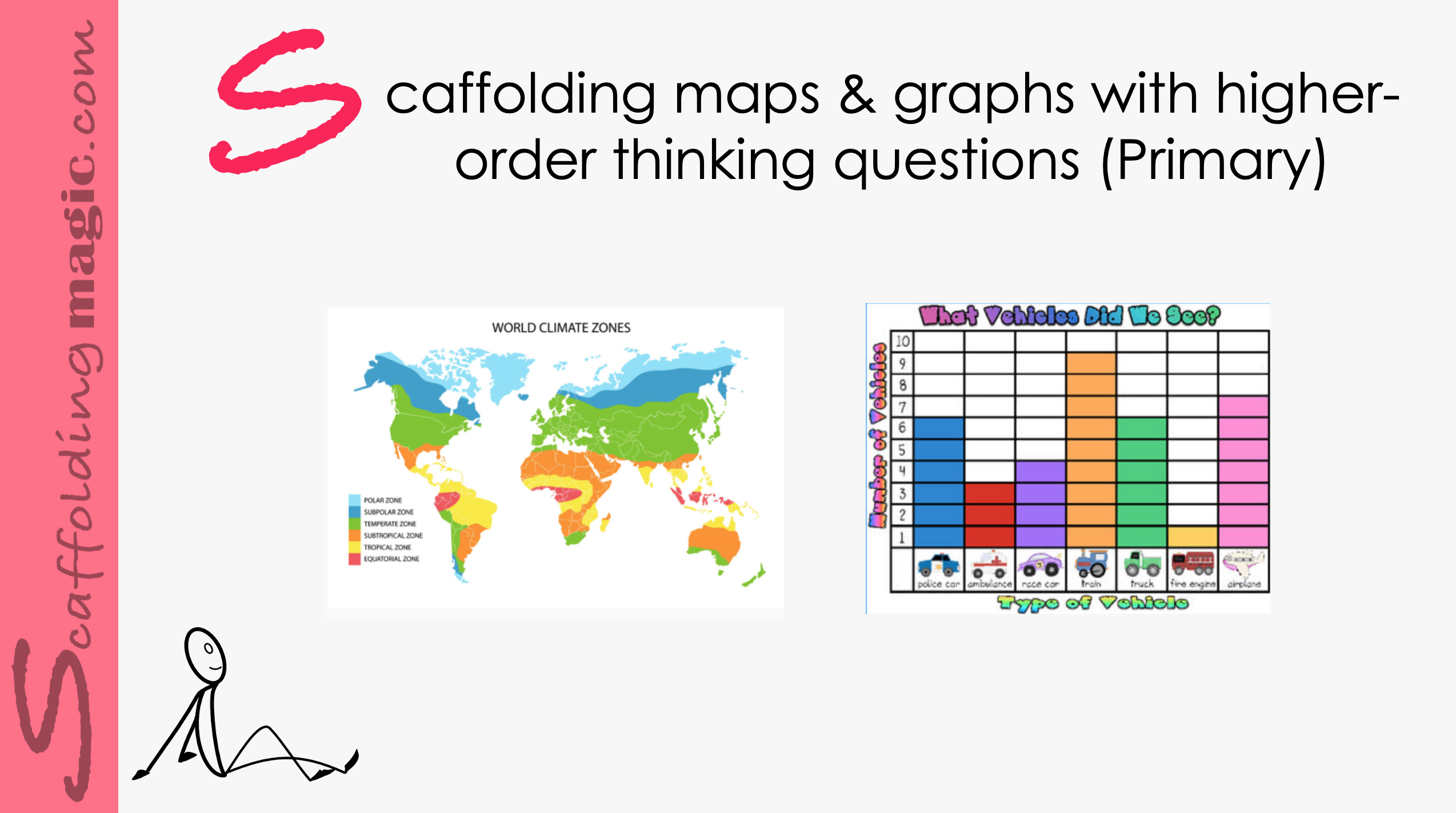
Higher-order level questions – those that elicit deeper thinking – help students to stretch their thinking and engage their curiosity, their reasoning ability, their creativity, and independence. These questions encourage students to open their minds, they offer opportunities to produce original thinking. A well-structured question sparks perspectives that might not have at first occurred to us; they encourage us to look at the issue from different perspectives. Higher-order level questions inspire fresh and sometimes even startling insights and ideas, they open roads for wider perspectives of the issue, and enable teachers and students to work together in constructing understanding. If we use effective questioning skills in the educational environment, we help our students to be more effective thinkers now and in the future.*
Scaffolding Maps and Graphs with Higher-Order Level Questions (Primary)
$5.00
Higher-order level questions – those that elicit deeper thinking – help students to stretch their thinking and engage their curiosity, their reasoning ability, their creativity, and independence. These questions encourage students to open their minds, they offer opportunities to produce original thinking. A well-structured question sparks perspectives that might not have at first occurred to us; they encourage us to look at the issue from different perspectives. Higher-order level questions inspire fresh and sometimes even startling insights and ideas, they open roads for wider perspectives of the issue, and enable teachers and students to work together in constructing understanding. If we use effective questioning skills in the educational environment, we help our students to be more effective thinkers now and in the future.*
Related products
-
Primary ScaffoldsQuick View
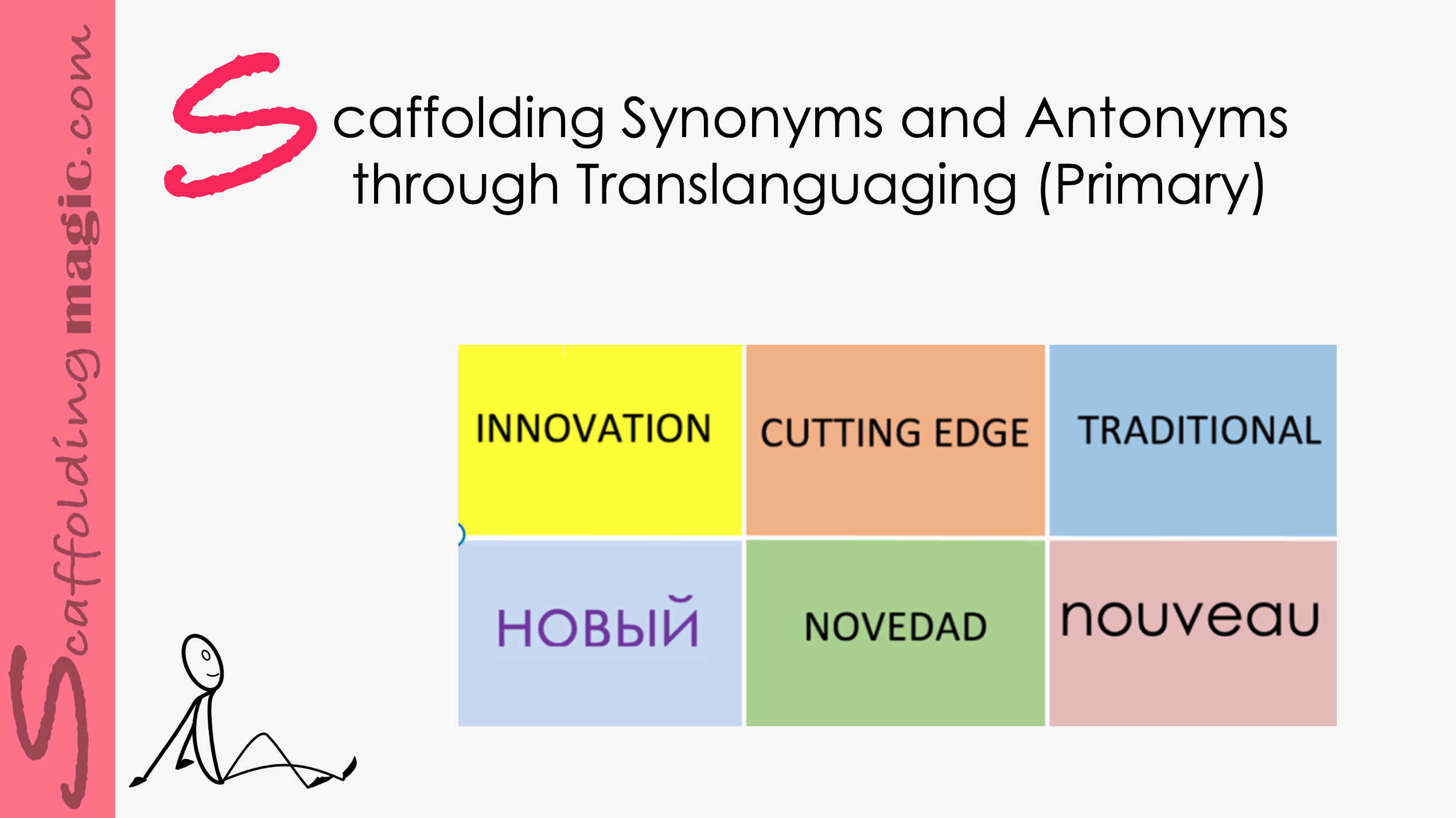
Scaffolding Synonyms and Antonyms through Translanguaging (Primary)
$5.00 Add to cartRated 0 out of 5 -
Primary ScaffoldsQuick View
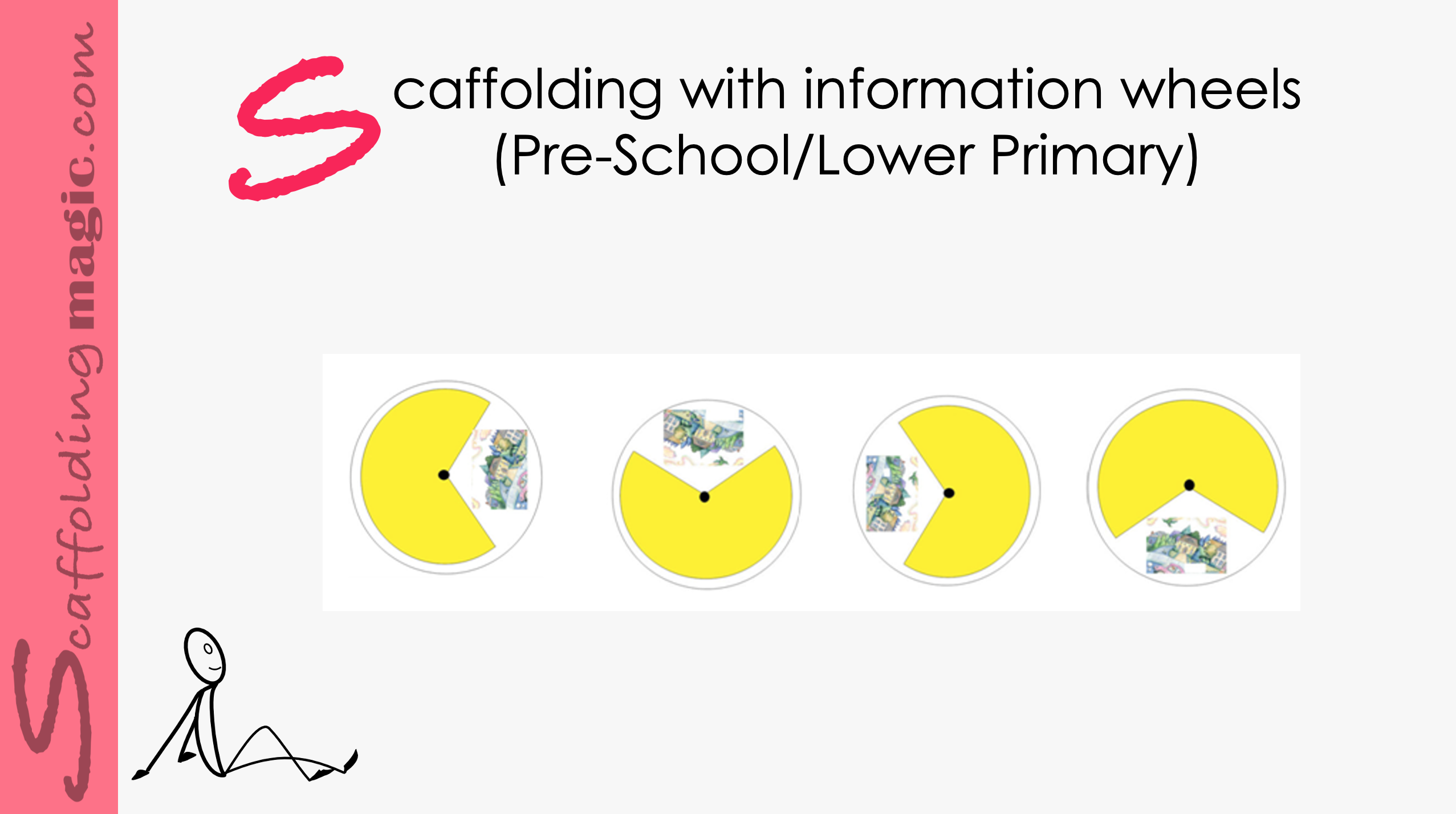
Scaffolding with Information Wheels (Pre-school/lower primary)
$5.00 Add to cartRated 0 out of 5 -
Primary ScaffoldsQuick View
Scaffolding International Thank You Day (Primary)
$5.00 Add to cartRated 0 out of 5 -
Primary ScaffoldsQuick View
Scaffolding Academic Language with ‘What’s Missing?’ (Pre-School/Lower Primary)
$5.00 Add to cartRated 0 out of 5
Scaffolding Synonyms and Antonyms through Translanguaging (Primary)
An important factor in translanguaging is knowing the different registers – when to use different tones, words, phrases. It’s important to know which terms are appropriate for specific circumstances. Especially in those languages (such as English) in which there is no formal or informal pronouns, register and tone transmit crucial information. To give our students an even wider prospects in their scholastic and professional lives, being comfortable with – or at least recognising – register is of the highest importance.
An important factor in translanguaging is knowing the different registers – when to use different tones, words, phrases. It’s important to know which terms are appropriate for specific circumstances. Especially in those languages (such as English) in which there is no formal or informal pronouns, register and tone transmit crucial information. To give our students an even wider prospects in their scholastic and professional lives, being comfortable with – or at least recognising – register is of the highest importance.
Scaffolding with Information Wheels (Pre-school/lower primary)
Using information wheels in lessons is a wonderful way of giving our students the opportunity to learn through, among other learning styles, kinesthetic interaction. They’ll be pulling from past knowledge, using deductive reasoning, negotiating meaning, and learning new subject matter, all at the same time. Studies show that learning is enhanced when students acquire knowledge through active processes that engage them. Literacy is a combination of recognising and matching oral and written language. The most effective ways of promoting literacy is to make vocabulary visible and to create high encounters with these words for your students – in interactive ways. Using wheels to scaffold vocabulary before you read a story can help. Below you’ll see how you can help your students to match words with images with an information wheel. information wheel.
Using information wheels in lessons is a wonderful way of giving our students the opportunity to learn through, among other learning styles, kinesthetic interaction. They’ll be pulling from past knowledge, using deductive reasoning, negotiating meaning, and learning new subject matter, all at the same time. Studies showthat learning is enhanced when students acquire knowledge through active processes that engage them. Literacy is a combination of recognising and matching oral and written language. The most effective ways of promoting literacy is to make vocabulary visible and to create high encounters with these words for your students – in interactive ways. Using wheels to scaffold vocabulary before you read a story can help. Below you’ll see how you can help your students to match words with images with an information wheel. information wheel.
Scaffolding International Thank You Day (Primary)
The International Thank You Day – celebrated by many on January 11th, others on June 11th – is a wonderful opportunity to help our students to focus on gratitude and add to positive forces in the world. Including gratitude in the educational environments is proven to improve relationships both in and outside of the classroom. Stressing affective factors in our lessons aligns us Vygotsky’s assertion (1978) that our students are more likely to step outside their comfort zone (ZPD) when they feel that they are supported and nurtured.
The International Thank You Day – celebrated by many on January 11th, others on June 11th – is a wonderful opportunity to help our students to focus on gratitude and add to positive forces in the world. Including gratitude in the educational environments is proven to improve relationships both in and outside of the classroom. Stressing affective factors in our lessons aligns us Vygotsky’s assertion (1978) that our students are more likely to step outside their comfort zone (ZPD) when they feel that they are supported and nurtured.
Scaffolding Academic Language with ‘What’s Missing?’ (Pre-School/Lower Primary)
Academic language is so important that experts assert that the warehouse of words a person has stored away is directly connected to their quality of thinking: higher quality of words equals higher quality of thinking.** In this age of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the quality of thinking our students reach in our classes, will be the difference between being qualified for jobs that technology is (still) not capable of performing, and watching the world from the sidelines.
This applies even to our youngest learners. We can help them to assimilate academic language even before they begin to read. If we verbalise first-, second- and third-tier words,*** through dynamic activities, we are helping them to become familiar with academic language that will serve them for the rest of their academic and professional lives.
Academic language is so important that experts assert that the warehouse of words a person has stored away is directly connected to their quality of thinking: higher quality of words equals higher quality of thinking.** In this age of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the quality of thinking our students reach in our classes, will be the difference between being qualified for jobs that technology is (still) not capable of performing, and watching the world from the sidelines.
This applies even to our youngest learners. We can help them to assimilate academic language even before they begin to read. If we verbalise first-, second- and third-tier words,*** through dynamic activities, we are helping them to become familiar with academic language that will serve them for the rest of their academic and professional lives.