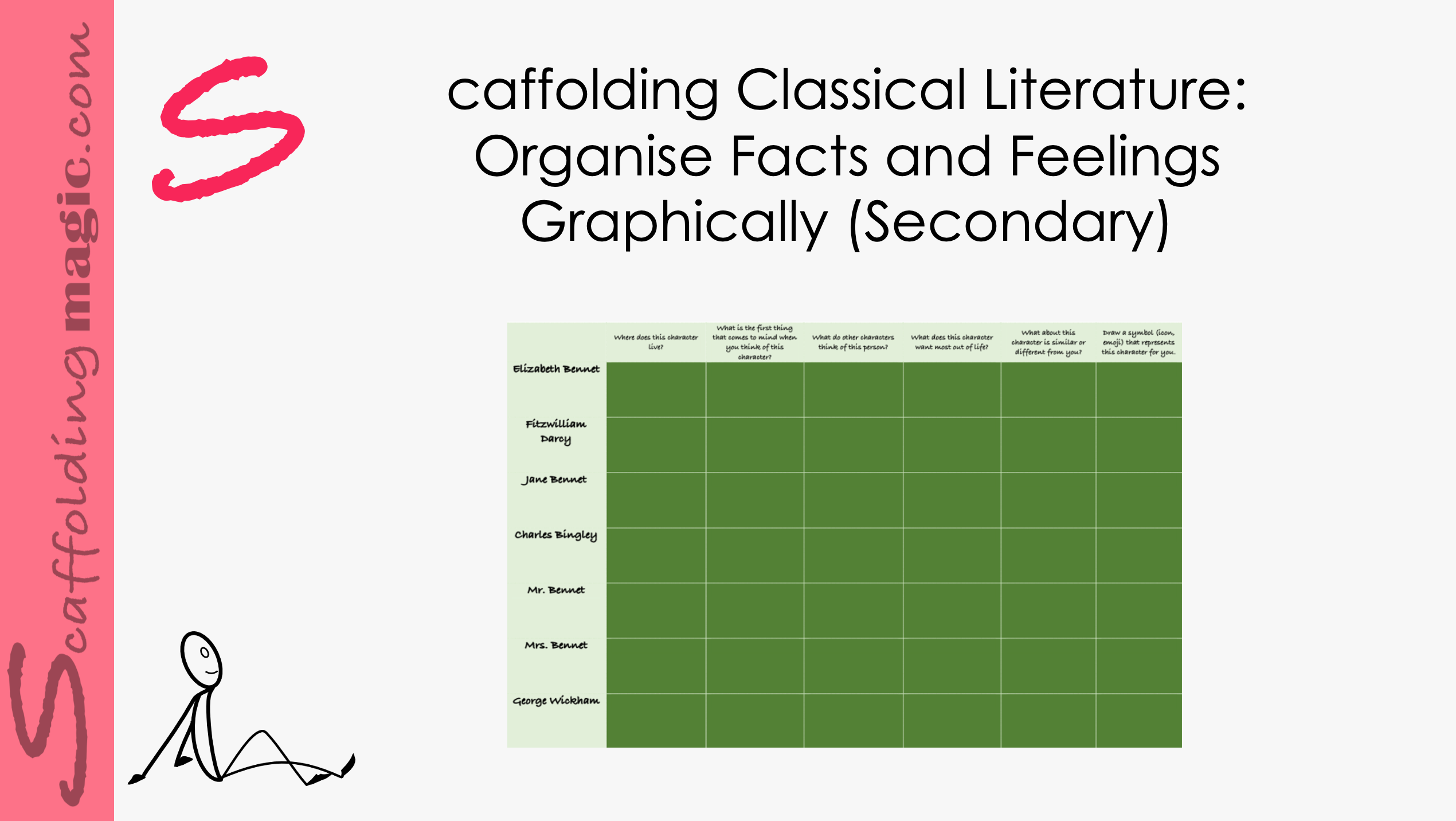
Here is a scaffold that will help your students keep track of the many characters in the story. Aside from the facts and family trees which can help enormously in following the plot, the graph encourages the students to pay attention to personalities and actions so they can make connections to them and people in their own lives – a key in engaging our students.
Scaffolding Activity for Classic Literature 4: Organise Facts and Feelings Graphically
$5.00
Here is a scaffold that will help your students keep track of the many characters in the story. Aside from the facts and family trees which can help enormously in following the plot, the graph encourages the students to pay attention to personalities and actions so they can make connections to them and people in their own lives – a key in engaging our students.
Related products
-
Secondary ScaffoldsQuick View
Scaffolding Challenging Terms and Academic Language
$5.00 Add to cartRated 0 out of 5 - Quick View
-
Secondary ScaffoldsQuick View
Scaffolding by Enriching the Sequencing Dynamic (Secondary)
$5.00 Add to cartRated 0 out of 5 -
Secondary ScaffoldsQuick View
Scaffolding Maps & Graphs with Higher-Order Level Questions (Secondary)
$20.00 Add to cartRated 0 out of 5
Scaffolding Challenging Terms and Academic Language
Developing new academic language can be challenging for students in any language. If the terms or vocabulary are intrinsic to a successful interaction of the task, we need to make a bit of extra effort to give our students support so they feel more confident about their understanding and usage of the language. Scaffolding techniques can help students bridge gaps so that they can engage in challenging units with more ease.
This scaffold integrates images and linguistics giving students support in different learning styles. They learn the parameters of a term experientially, using vocabulary that is provided, discerning differences in images and paying close attention to details in the information given. Critical thinking, multiple possibilities for recognising truths, and verbalisation will engage your students in a powerful collaborative activity towards new knowledge.
Developing new academic language can be challenging for students in any language. If the terms or vocabulary are intrinsic to a successful interaction of the task, we need to make a bit of extra effort to give our students support so they feel more confident about their understanding and usage of the language. Scaffolding techniques can help students bridge gaps so that they can engage in challenging units with more ease.
This scaffold integrates images and linguistics giving students support in different learning styles. They learn the parameters of a term experientially, using vocabulary that is provided, discerning differences in images and paying close attention to details in the information given. Critical thinking, multiple possibilities for recognising truths, and verbalisation will engage your students in a powerful collaborative activity towards new knowledge.
Scaffolding Classical Literature with Tabu
Many ESL teachers will questions the importance of teaching and using classic literature in their classes. We probably all agree that it is not easy to teach in its authentic form as it demands a high level of language proficiency and maturity for any student, and especially students those whose home language is different from that of the class text.
Nevertheless, through varied techniques, the reading of authentic classic literature is an incredibly enriching experience (although your students may not appreciate or admit this until years later!). Gamify the learning and you have students begging for more!!!
Many ESL teachers will questions the importance of teaching and using classic literature in their classes. We probably all agree that it is not easy to teach in its authentic form as it demands a high level of language proficiency and maturity for any student, and especially students those whose home language is different from that of the class text.
Nevertheless, through varied techniques, the reading of authentic classic literature is an incredibly enriching experience (although your students may not appreciate or admit this until years later!). Gamify the learning and you have students begging for more!!!
Scaffolding by Enriching the Sequencing Dynamic (Secondary)
Sequencing is a concept that needs to be repeated throughout the education process. We need to intentionally give our students the opportunities to be able to recognise and express sequences, and we need to provide the phrases they can use to clarify the ordering of events. It might be motivating to know that studies show that students are able to recall information more accurately if they’ve been schooled in sequencing.
Sequencing is a concept that needs to be repeated throughout the education process. We need to intentionally give our students the opportunities to be able to recognise and express sequences, and we need to provide the phrases they can use to clarify the ordering of events. It might be motivating to know that studies show that students are able to recall information more accurately if they´ve been schooled in sequencing.
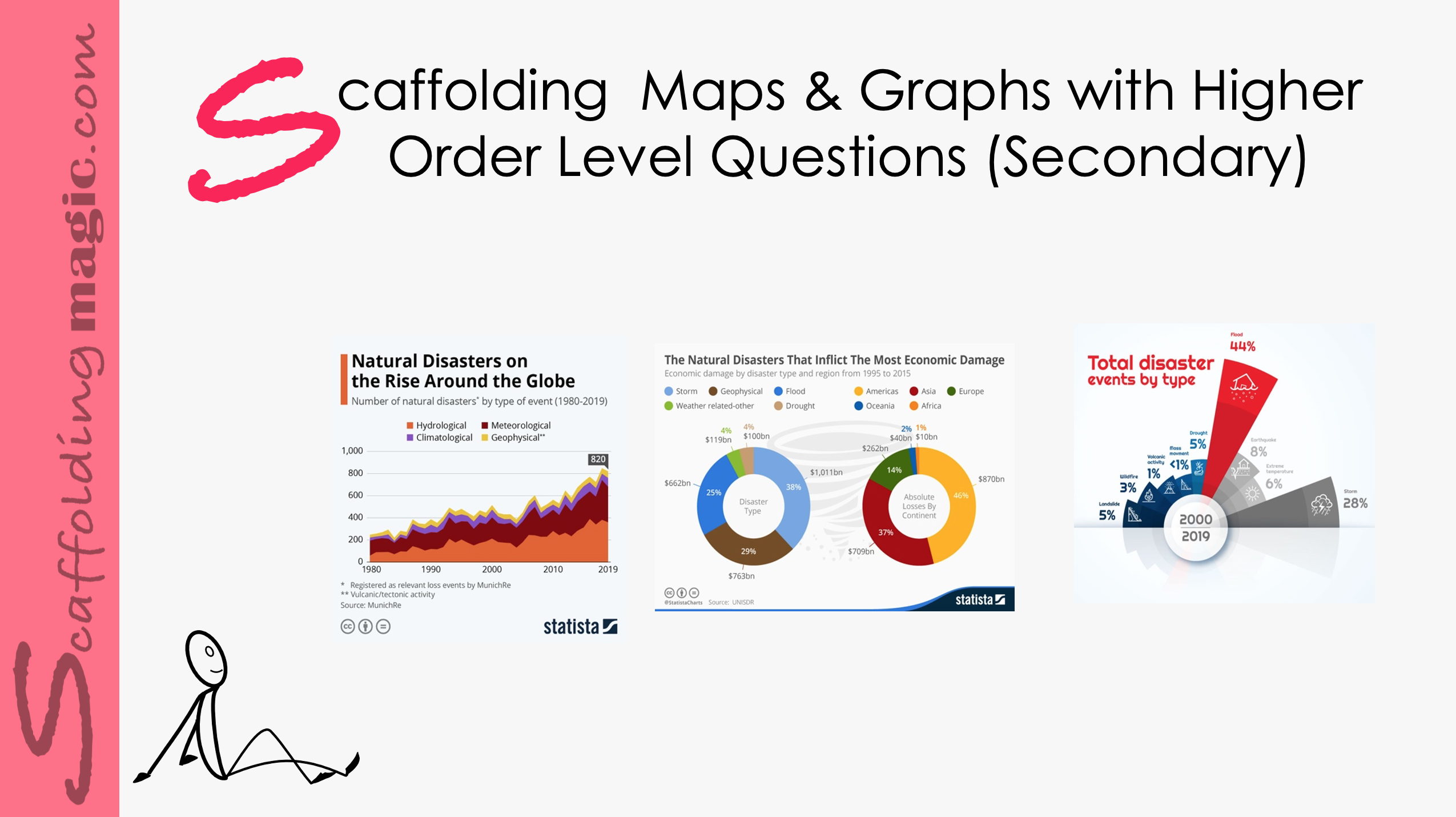
Scaffolding Maps & Graphs with Higher-Order Level Questions (Secondary)
Higher-order level questions – those that elicit deeper thinking – help students to stretch their thinking and engage their curiosity, their reasoning ability, their creativity, and independence. These questions encourage students to open their minds, they offer opportunities to produce original thinking. A well-structured question sparks perspectives that might not have at first occurred to us; they encourage us to look at the issue from different perspectives. Higher-order level questions inspire fresh and sometimes even startling insights and ideas, they open roads for wider perspectives of the issue, and enable teachers and students to work together in constructing understanding. If we use effective questioning skills in the educational environment, we help our students to be more effective thinkers now and in the future.*
Higher-order level questions – those that elicit deeper thinking – help students to stretch their thinking and engage their curiosity, their reasoning ability, their creativity, and independence. These questions encourage students to open their minds, they offer opportunities to produce original thinking. A well-structured question sparks perspectives that might not have at first occurred to us; they encourage us to look at the issue from different perspectives. Higher-order level questions inspire fresh and sometimes even startling insights and ideas, they open roads for wider perspectives of the issue, and enable teachers and students to work together in constructing understanding. If we use effective questioning skills in the educational environment, we help our students to be more effective thinkers now and in the future.*