The ability to switch perspective is essential to learning in every domain. For those who follow Deepak Chopra and his deeply rooted scientific conclusions regarding the human condition, the more effort we make in seeing a situation through the perspective of someone we are offended by or disagree with, the more we heal on a cellular level – both emotionally and physically. Students are going to read chunks of dialogue taken from various tracks.
Scaffolding Dialogue for Videos, Movies, Podcasts, Plays (Secondary)
$5.00
The ability to switch perspective is essential to learning in every domain. For those who follow Deepak Chopra and his deeply rooted scientific conclusions regarding the human condition, the more effort we make in seeing a situation through the perspective of someone we are offended by or disagree with, the more we heal on a cellular level – both emotionally and physically. Students are going to read chunks of dialogue taken from various tracks.
Related products
- Quick View
-
Secondary ScaffoldsQuick View
Scaffolding Maps & Graphs with Higher-Order Level Questions (Secondary)
$20.00 Add to cartRated 0 out of 5 - Quick View
-
Secondary ScaffoldsQuick View
Scaffolding Writing to Elicit Empathy (Secondary)
$5.00 Add to cartRated 0 out of 5
Scaffolding Texts in Thirds (Secondary)
This scaffold presents one technique you can use to combat this human tendency of laziness – of relying on memory instead of working actively to further knowledge. We use here a social science lesson on global migration, and you’ll see how you can adapt it to any lesson you’re about to begin.
This scaffold presents one technique you can use to combat this human tendency of laziness – of relying on memory instead of working actively to further knowledge. We use here a social science lesson on global migration, and you’ll see how you can adapt it to any lesson you’re about to begin.
janice added this to see
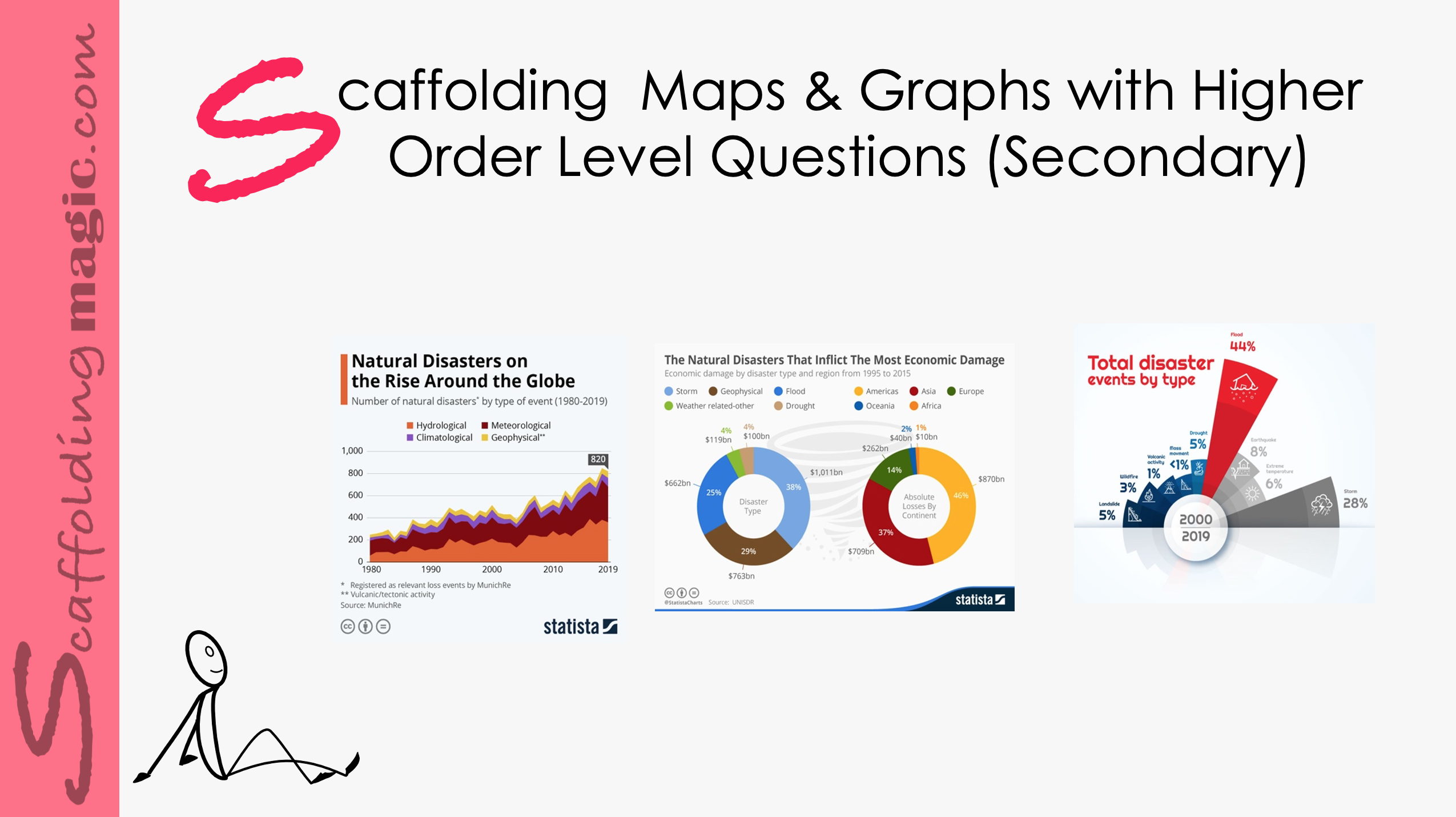
Scaffolding Maps & Graphs with Higher-Order Level Questions (Secondary)
Higher-order level questions – those that elicit deeper thinking – help students to stretch their thinking and engage their curiosity, their reasoning ability, their creativity, and independence. These questions encourage students to open their minds, they offer opportunities to produce original thinking. A well-structured question sparks perspectives that might not have at first occurred to us; they encourage us to look at the issue from different perspectives. Higher-order level questions inspire fresh and sometimes even startling insights and ideas, they open roads for wider perspectives of the issue, and enable teachers and students to work together in constructing understanding. If we use effective questioning skills in the educational environment, we help our students to be more effective thinkers now and in the future.*
Higher-order level questions – those that elicit deeper thinking – help students to stretch their thinking and engage their curiosity, their reasoning ability, their creativity, and independence. These questions encourage students to open their minds, they offer opportunities to produce original thinking. A well-structured question sparks perspectives that might not have at first occurred to us; they encourage us to look at the issue from different perspectives. Higher-order level questions inspire fresh and sometimes even startling insights and ideas, they open roads for wider perspectives of the issue, and enable teachers and students to work together in constructing understanding. If we use effective questioning skills in the educational environment, we help our students to be more effective thinkers now and in the future.*
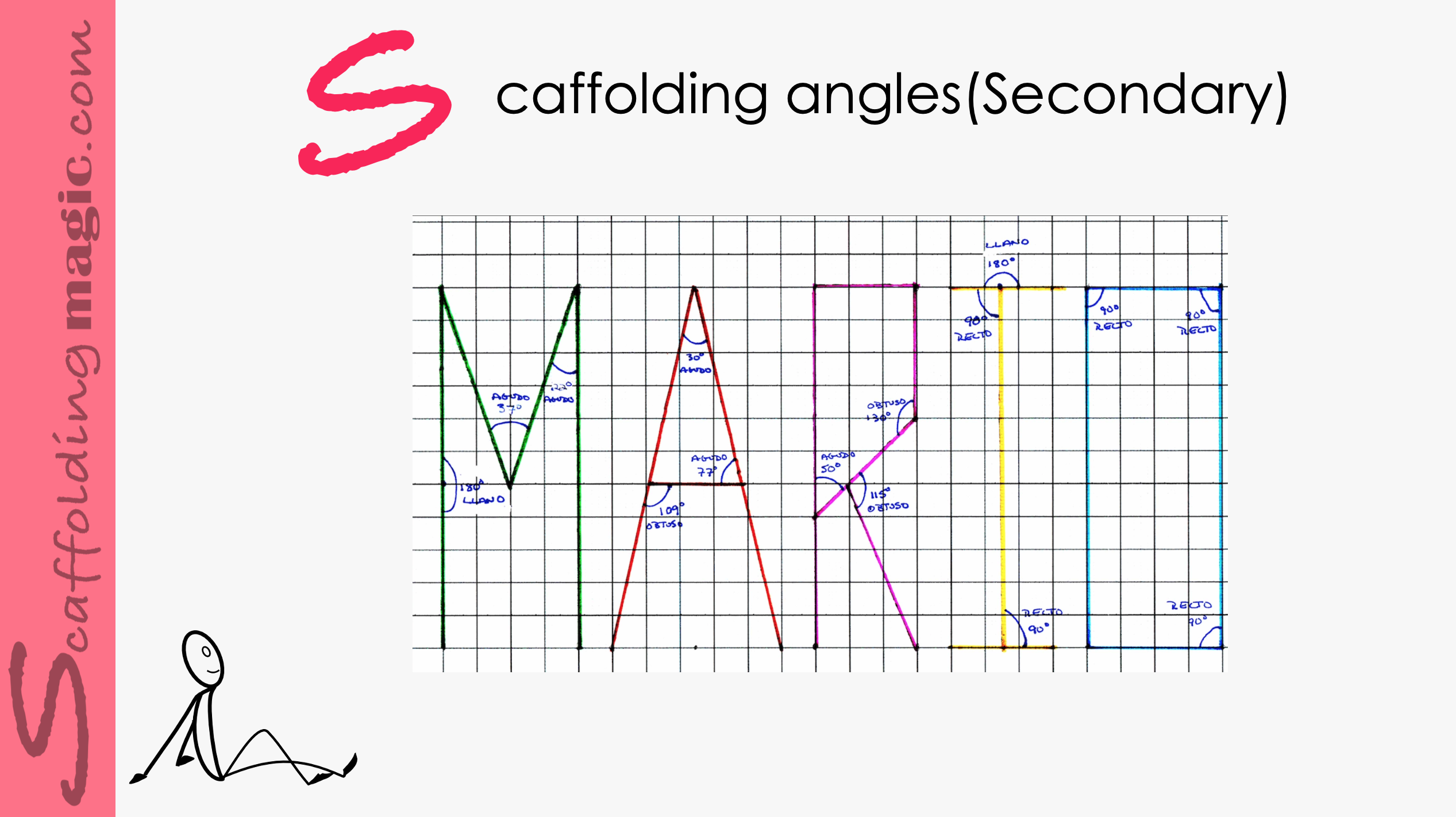
Scaffolding Angles (Secondary)
If you have students who are more linguistic, more in touch with Humanities, more comfortable with words or music or the arts, it’s possible that they haven’t found a way to embrace numbers or see their relance in their lives. For a maths teacher or students who are passionate about numbers, this seems unfathomable. Numbers are glorious! Numbers determine practically all of our decisions (probability, fractions, percentages, etc.). How can you feel so indifferent to educating yourself about such a fascinating and useful branch of study?
Scaffolding Writing to Elicit Empathy (Secondary)
Writing is one of the four cornerstone skills of every inclusive educational curriculum. It helps us form our thoughts into coherent verses and communicate over distance and time. It is a skill usually approached as a way of appeasing bands for standardised exams, but, in fact, is the perfect tool to foster the development and expression of empathy.
Writing is one of the four cornerstone skills of every inclusive educational curriculum. It helps us form our thoughts into coherent verses and communicate over distance and time. It is a skill usually approached as a way of appeasing bands for standardised exams, but, in fact, is the perfect tool to foster the development and expression of empathy.