Using information wheels in lessons is a wonderful way of honouring our students who need to learn through kinesthetic interaction. With information wheels, your students will use deductive reasoning, negotiate meaning, activate long-term memory, and learn new subject matter, all at the same time. Because they will be interacting with information with their hands, they’ll benefit from the essential transition from social-to-exploratory-to dialogic-to presentational-and…finally…to meta learning.*
Scaffolding with Information Wheels (Higher Education)
$5.00
Using information wheels in lessons is a wonderful way of honouring our students who need to learn through kinesthetic interaction. With information wheels, your students will use deductive reasoning, negotiate meaning, activate long-term memory, and learn new subject matter, all at the same time. Because they will be interacting with information with their hands, they’ll benefit from the essential transition from social-to-exploratory-to dialogic-to presentational-and…finally…to meta learning.*
Related products
-
Higher Education ScaffoldsQuick View
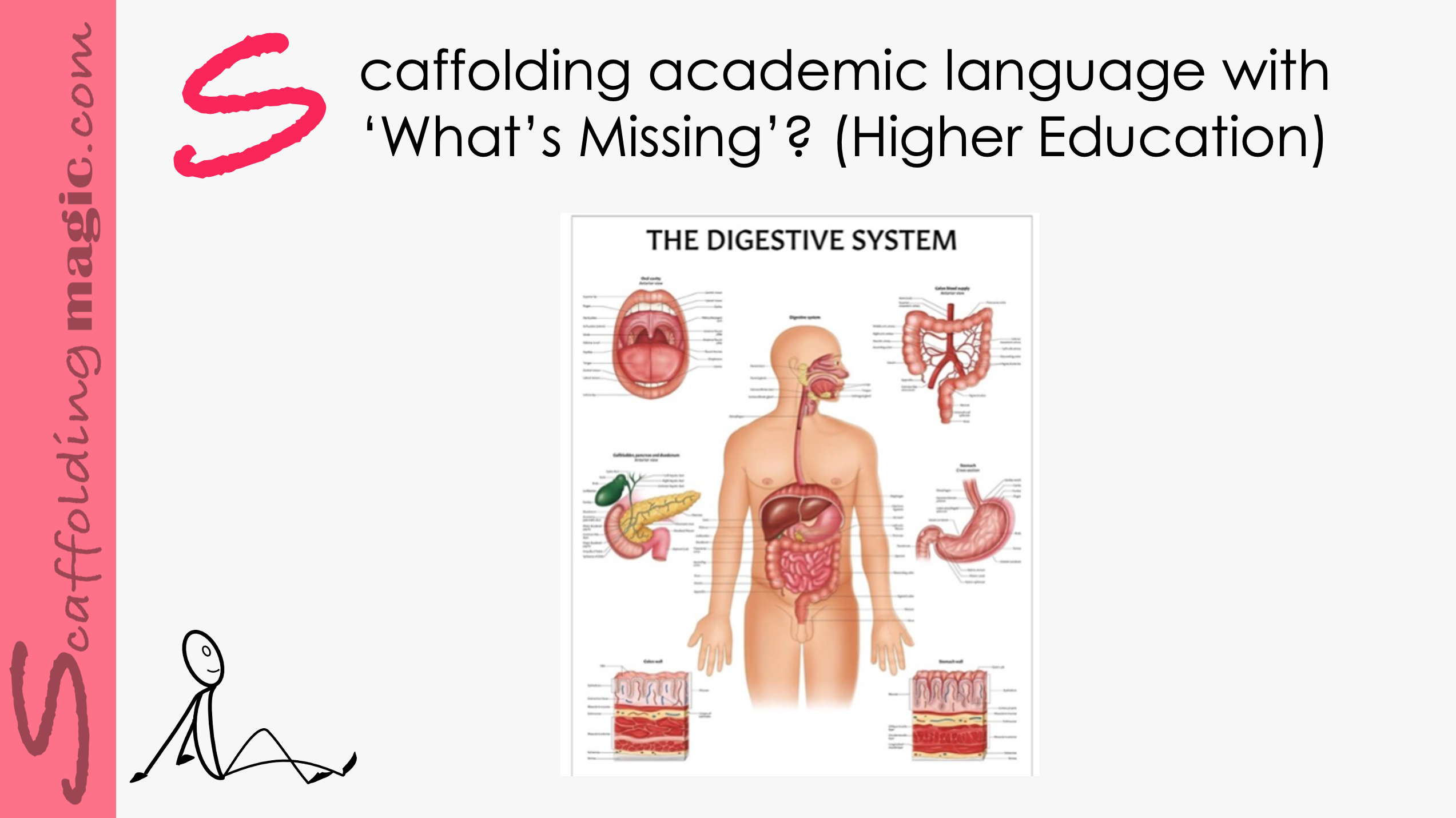
Scaffolding Academic Language with ‘What’s Missing?’ (Higher Education)
$5.00 Add to cartRated 0 out of 5 -
Higher Education ScaffoldsQuick View
Scaffolding Visual Information in Strips (Higher Education)
$5.00 Add to cartRated 0 out of 5 -
Higher Education ScaffoldsQuick View
Scaffolding Images and Text with Mini-Cards (Higher Education)
$5.00 Add to cartRated 0 out of 5 - Quick View
Scaffolding Academic Language with ‘What’s Missing?’ (Higher Education)
This scaffold address the importance of academic language, which is so important that experts assert that the warehouse of words a person has stored away is directly connected to their quality of thinking: higher quality of words equals higher quality of thinking.** In this age of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the quality of thinking our students reach in our classes, will be the difference between being qualified for jobs that technology is (still) not capable of performing, and watching the world from the sidelines.
This scaffold address the importance of academic language, which is so important that experts assert that the warehouse of words a person has stored away is directly connected to their quality of thinking: higher quality of words equals higher quality of thinking.** In this age of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the quality of thinking our students reach in our classes, will be the difference between being qualified for jobs that technology is (still) not capable of performing, and watching the world from the sidelines.
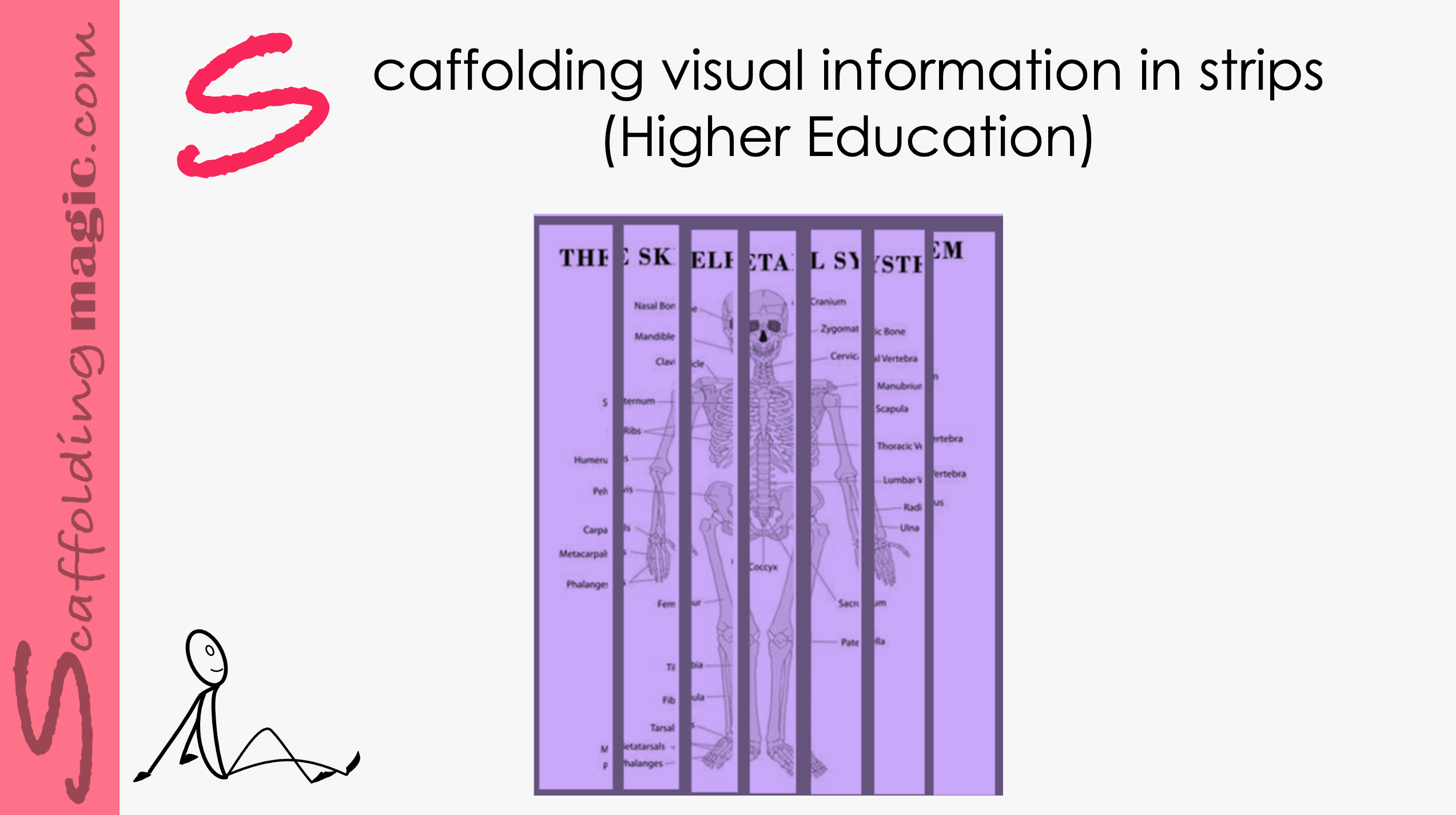
Scaffolding Visual Information in Strips (Higher Education)
When we add strategies in activities that promote critical thinking, collaboration, negotiation and prediction – all through visual means – we’ve created a powerful means of presenting new ideas to our students. This scaffold technique also includes categorisation which, according to Morton Hunt*, one of the pioneers of the study of the mind, has been proven to yield educational efficiency and helps the brain process information more fluidly.
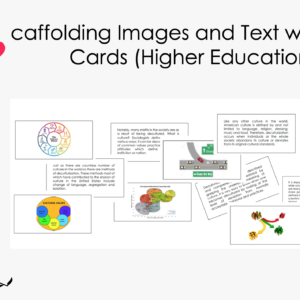
Scaffolding Images and Text with Mini-Cards (Higher Education)
In this scaffold, students have the opportunity to develop their linguistic and visual skills as they negotiate connections between text and images. They also interact with the information through temporal and grammatical transformations, as well as bodily-kinesthetic interplay.
We take every opportunity to expand our practice. Whenever possible, we broaden the variety of strategies we use in our classroom activities so that when our students go out into the world, they are more prepared – all because of the extra effort we put into our lessons.
In this scaffold, students have the opportunity to develop their linguistic and visual skills as they negotiate connections between text and images. They also interact with the information through temporal and grammatical transformations, as well as bodily-kinesthetic interplay.
We take every opportunity to expand our practice. Whenever possible, we broaden the variety of strategies we use in our classroom activities so that when our students go out into the world, they are more prepared – all because of the extra effort we put into our lessons.
Janice’s new product for testing
Now on to the short description with a pdf added to the product gallery
I want to see how this will show up, so I’ve added a new product to play with.
How do the images appear, etc.