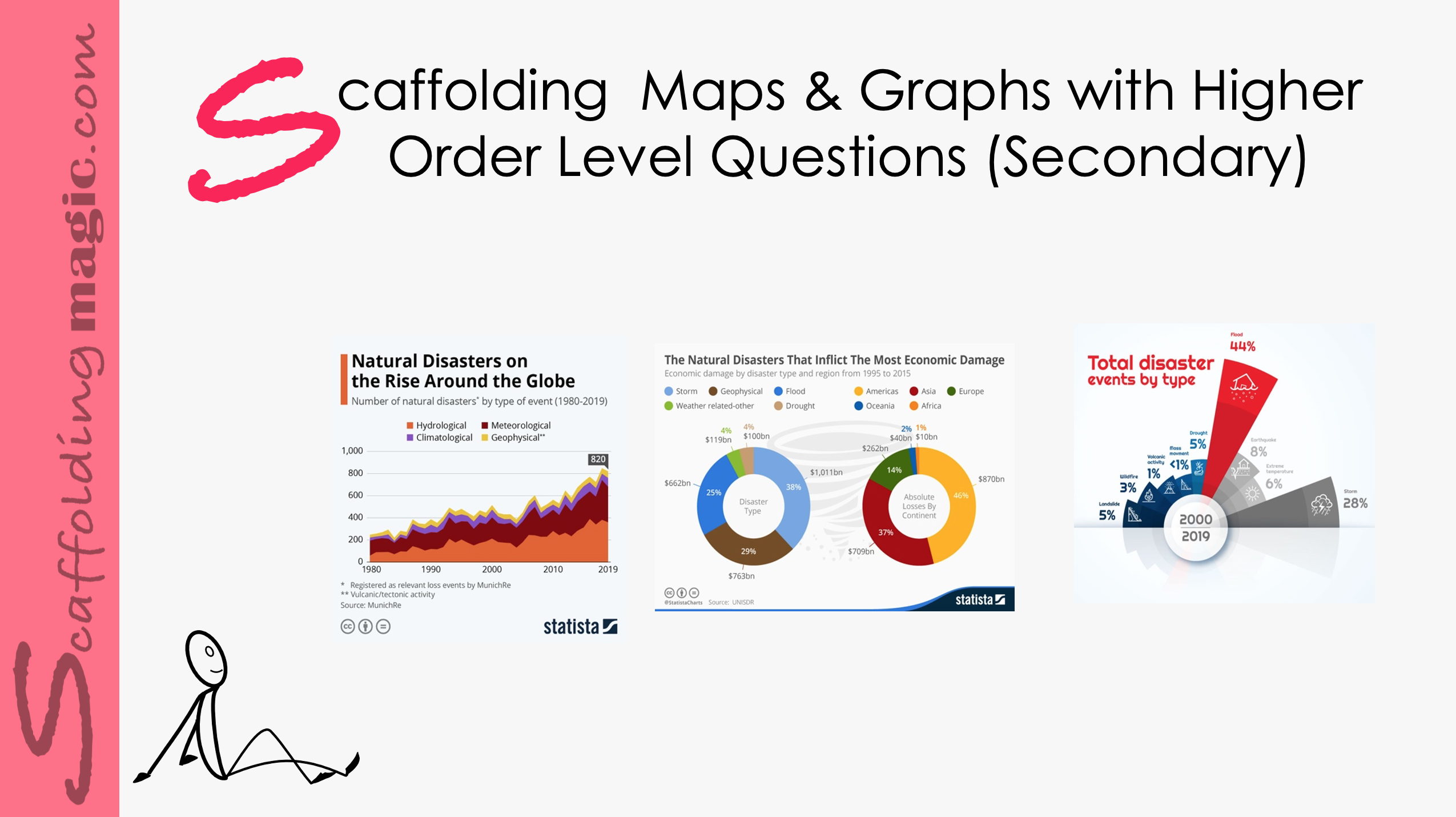
Higher-order level questions – those that elicit deeper thinking – help students to stretch their thinking and engage their curiosity, their reasoning ability, their creativity, and independence. These questions encourage students to open their minds, they offer opportunities to produce original thinking. A well-structured question sparks perspectives that might not have at first occurred to us; they encourage us to look at the issue from different perspectives. Higher-order level questions inspire fresh and sometimes even startling insights and ideas, they open roads for wider perspectives of the issue, and enable teachers and students to work together in constructing understanding. If we use effective questioning skills in the educational environment, we help our students to be more effective thinkers now and in the future.*
Scaffolding Maps & Graphs with Higher-Order Level Questions (Secondary)
$20.00
Higher-order level questions – those that elicit deeper thinking – help students to stretch their thinking and engage their curiosity, their reasoning ability, their creativity, and independence. These questions encourage students to open their minds, they offer opportunities to produce original thinking. A well-structured question sparks perspectives that might not have at first occurred to us; they encourage us to look at the issue from different perspectives. Higher-order level questions inspire fresh and sometimes even startling insights and ideas, they open roads for wider perspectives of the issue, and enable teachers and students to work together in constructing understanding. If we use effective questioning skills in the educational environment, we help our students to be more effective thinkers now and in the future.*
Related products
-
Secondary ScaffoldsQuick View
Scaffolding Challenging Terms and Academic Language
$5.00 Add to cartRated 0 out of 5 - Quick View
-
Secondary ScaffoldsQuick View
Scaffolding by Enriching the Sequencing Dynamic (Secondary)
$5.00 Add to cartRated 0 out of 5 - Quick View
Scaffolding Challenging Terms and Academic Language
Developing new academic language can be challenging for students in any language. If the terms or vocabulary are intrinsic to a successful interaction of the task, we need to make a bit of extra effort to give our students support so they feel more confident about their understanding and usage of the language. Scaffolding techniques can help students bridge gaps so that they can engage in challenging units with more ease.
This scaffold integrates images and linguistics giving students support in different learning styles. They learn the parameters of a term experientially, using vocabulary that is provided, discerning differences in images and paying close attention to details in the information given. Critical thinking, multiple possibilities for recognising truths, and verbalisation will engage your students in a powerful collaborative activity towards new knowledge.
Developing new academic language can be challenging for students in any language. If the terms or vocabulary are intrinsic to a successful interaction of the task, we need to make a bit of extra effort to give our students support so they feel more confident about their understanding and usage of the language. Scaffolding techniques can help students bridge gaps so that they can engage in challenging units with more ease.
This scaffold integrates images and linguistics giving students support in different learning styles. They learn the parameters of a term experientially, using vocabulary that is provided, discerning differences in images and paying close attention to details in the information given. Critical thinking, multiple possibilities for recognising truths, and verbalisation will engage your students in a powerful collaborative activity towards new knowledge.
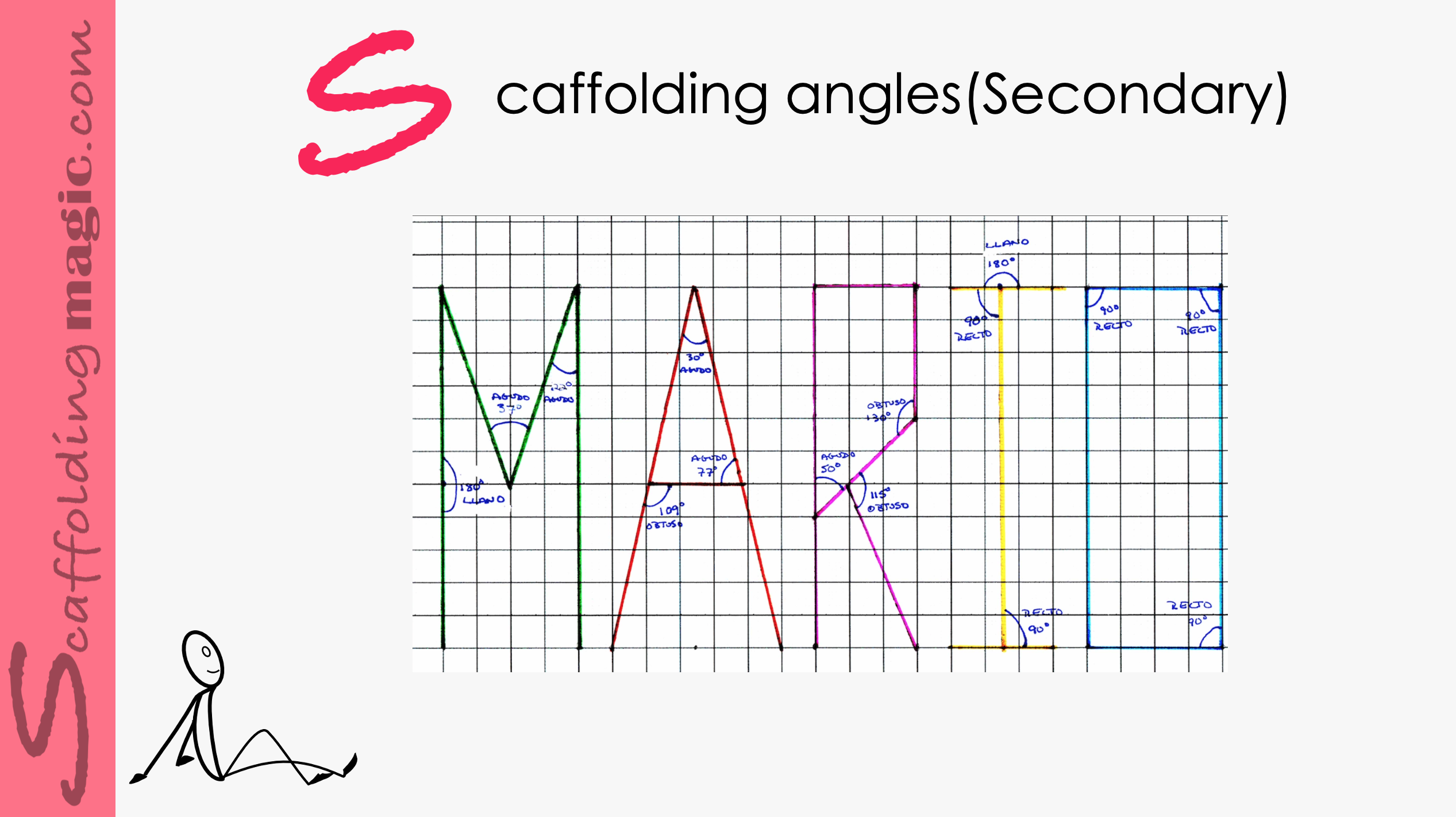
Scaffolding Angles (Secondary)
If you have students who are more linguistic, more in touch with Humanities, more comfortable with words or music or the arts, it’s possible that they haven’t found a way to embrace numbers or see their relance in their lives. For a maths teacher or students who are passionate about numbers, this seems unfathomable. Numbers are glorious! Numbers determine practically all of our decisions (probability, fractions, percentages, etc.). How can you feel so indifferent to educating yourself about such a fascinating and useful branch of study?
Scaffolding by Enriching the Sequencing Dynamic (Secondary)
Sequencing is a concept that needs to be repeated throughout the education process. We need to intentionally give our students the opportunities to be able to recognise and express sequences, and we need to provide the phrases they can use to clarify the ordering of events. It might be motivating to know that studies show that students are able to recall information more accurately if they’ve been schooled in sequencing.
Sequencing is a concept that needs to be repeated throughout the education process. We need to intentionally give our students the opportunities to be able to recognise and express sequences, and we need to provide the phrases they can use to clarify the ordering of events. It might be motivating to know that studies show that students are able to recall information more accurately if they´ve been schooled in sequencing.
Scaffolding Human Rights (Secondary)
March 25th is the International Day of Remembrance of the Victims of Slavery and the Transatlantic Slave Trade. As educators, it’s vital for us to pass on bits of history so that even our youngest learners can internalise the injustice of what happened, in order to create more hope for the human population of today. Most history texts are written in depersonalised structures (passive tense with no recognisable narrator’s voice), and so are divorced from a tangible context that we usually need to connect to the information. Let’s add humanity and feeling to history so that our students see the connection to what happened in the past, their reality, and what they can do to make positive changes in the future.
March 25th is the International Day of Remembrance of the Victims of Slavery and the Transatlantic Slave Trade. As educators, it’s vital for us to pass on bits of history so that even our youngest learners can internalise the injustice of what happened, in order to create more hope for the human population of today. Most history texts are written in depersonalised structures (passive tense with no recognisible narrator’s voice), and so are divorced from a tangible context that we usually need to connect to the information. Let’s add humanity and feeling to history so that our students see the connection to what happened in the past, their reality, and what they can do to make positive changes in the future.